

Here, the economy is at point-A with Y1 level of output and P1 level of price. And this is mainly done through an increase in government spending or cut taxes.Īn increase in government spending directly affects the AD curve and on the other side, a cut in taxes will indirectly affect AD curve because consumers will have more money in their pockets after taxes.

THE GOAL OF EXPANSIONARY FISCAL POLICY IS FULL
the actual output is less than the potential output at full employment, then an expansionary fiscal policy can help to stimulate demand and shift the AD curve to the right. The aggregate demand curve shifts right.Īlso, if there is a recessionary gap in the economy i.e. This also stabilizes the employment in the economy and helps the economy to move out of the recession. Expansionary Fiscal PolicyĮxpansionary fiscal policy is enacted as a response to recessions or employment shocks through an increase in government spending on infrastructure, education, and unemployment benefits etc. There are two types of fiscal policy: Expansionary and Contractionary. Fiscal policy affects the growth rate of aggregate demand, given a constant growth in aggregate supply. Here, C= consumption Y = income, T = taxes, Y - T = disposable income, I= investment, G= government spending, NX= net exportsĬonsumption is a function of disposable income and assumes G and T are exogenous. Any change in the components gets reflected on the position and slope of the curve. The aggregate demand consists of consumption, investment, government spending and net exports. Therefore, any change in fiscal policy gets reflected on the aggregate demand curve. Fiscal policy affects the aggregate demand through an increase in expenditure or through taxes. The fiscal policy of a country generally focuses on increasing the growth rate of the economy and also keeping the inflation within limits. Fiscal policy aims at a stable economic growth and development for the country, full employment equilibrium, stability in prices and balance of payments equilibrium. spending of government on public goods and services and taxes. The tools of the government are government expenditures i.e. This can happen through changes in the level of taxation and government purchases in order to stimulate economic activities. It is an economic intervention by the government to change the policies that exist in the economy. Both of these policies are intended to increase aggregate demand while contributing to deficits or drawing down of budget surpluses.Fiscal policy is initiated by the legislative and/or the executive branches of government to change the direction of the economy. The two major examples of expansionary fiscal policy are tax cuts and increased government spending. Three problems that limit fiscal policy are delayed results, political pressures and changing spending levels.
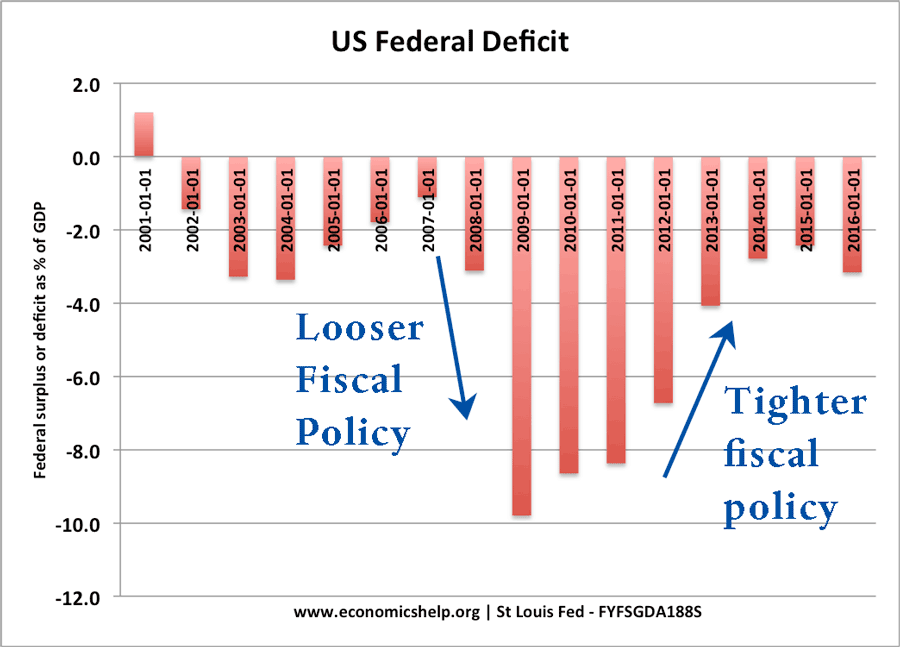
Moreover, what are three problems that limit fiscal policy? First, if the government increases its purchases but keeps taxes constant, it increases demand directly. A fiscal expansion, for example, raises aggregate demand through one of two channels. Likewise, what is the effect of fiscal policy? The most immediate effect of fiscal policy is to change the aggregate demand for goods and services. Limits of fiscal policy include difficulty of changing spending levels, predicting the future, delayed results, political pressures, and coordinating fiscal policy. Regarding this, what are the 5 limitations of fiscal policy? The disadvantages In trying to promote growth or create new jobs a fiscal stimulus through increased government spending can be inflationary, especially if the government has to borrow from the financial markets or if the spending is too fast, such as with an increase in current spending on wages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
